Most everyone on the planet has now heard of mRNA, thanks to the vaccines against Covid-19 from Pfizer and Moderna based on messenger RNA.
But before mRNA was used to address Covid, research was conducted into how it could fight cancer. Now, researchers at Ben-Gurion University of the Negev have discovered a key connection between mRNA, peptide proteins and tumor progression.
Messenger RNA codes for different proteins, each with a unique function. There are both “long” and “short” peptides. Until now, scientists were not sure if short peptides had any biological function.
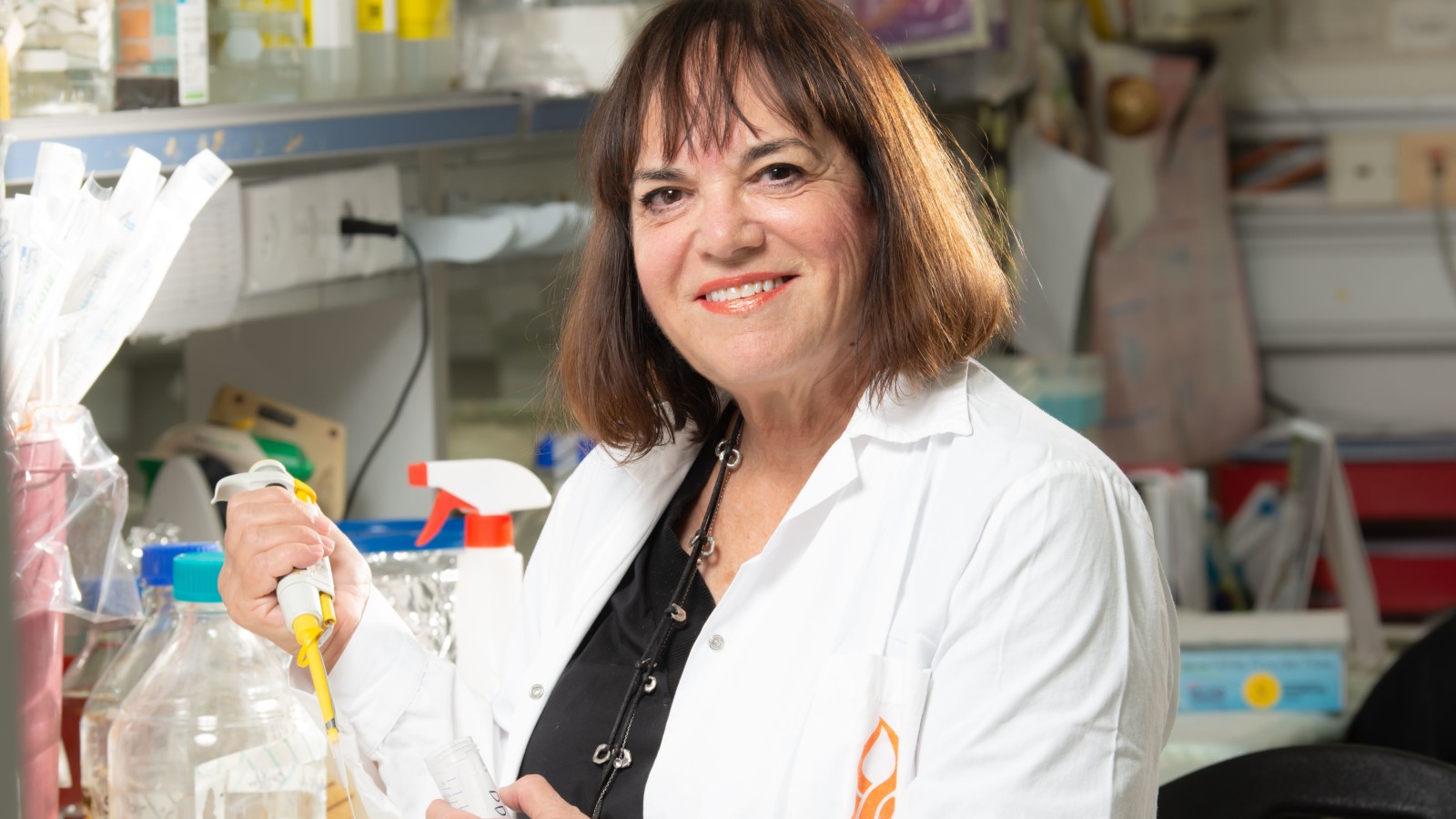
Prof. Etta Livneh of BGU’s Shraga Segal Department of Immunology, Microbiology, and Genetics has shown that single short peptides in fact have a very important role – as a kinase inhibitor that can slow tumor growth and invasion, cancer cell survival and metastasis.
Proteins (and protein kinases in particular) propagate signals that carry instructions to the cells and dictate cell fate. There are more than 500 different kinases in the human body.
With cancer, a kinase erroneously tells the cells to divide and reproduce in a rapid and uncontrollable manner. But the flipside is also true: If a kinase can be inhibited, it should block the proliferation of cancer cells.
And that’s “just the tip of the iceberg,” says Livneh, whose discovery has been a decade in the making. “Now that we know that at least some peptides have a biological function, we can begin to discover the roles of many more.”
Kinase inhibitors are already one of the hottest areas of cancer research, in some cases replacing chemotherapy. Livneh’s research will allow scientists to better understand how to control this vital cancer-fighting technology.
Livneh’s collaborators include Prof. Esti Yeger-Lotem from the Department of Clinical Biochemistry and Pharmacology at BGU and Prof. Moshe Elkabets in the Faculty of Health Sciences. Additional researchers include Divya Ram Jayaram, Sigal Frost, Chanan Argov, Vijayasteltar Belsamma Liju, Nikhil Ponnoor Anto, Amitha Muraleedharan, Assaf Ben-Ari, Rose Sinay, Ilan Smoly, Ofra Novoplansky, Noah Isakov, Dr. Debra Toiber and Chen Keasar.
The research was supported by a grant from the Israel Science Foundation and published in PNAS – Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America.